This learning proposal was created by a team of the Institut Josep Brugulat (Girona, Spain) secondary school teachers, and it’s shared under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Topic: Earth civilizations and life ecosystems
Area: Science, Technology, Engineering.
Abstract: In cooperative groups of 3 or 4, students must research and elaborate a new planetary system like our solar system. In addition, it must include at least one planet with similar characteristics to Earth (in order to be habitable) On this imagined planet will be developed a great historical civilization, analogous to the great civilizations: Mesopotamia & Egypt The project will conclude with an oral presentation to their peers by means of a model and a book
Learning objectives:
– Consolidate concepts about history and geographic features
– Consolidate concepts about biodiversity and conditions for life
– Put in action engineering and artistic skills by creating a new world model – Show initiative.
– Information research.
– Writing documents.
– Experimenting and being creative.
– Manual skills.
– Learning to work in a team.
Teachers’ profile: (team transversality)
– Social sciences
– Art
– Science
Advisable age of students: 12 – 13 years old
(Flexible according to the curriculum of specific country)
Attention to diversity and inclusion aspects to have in account:
– Learning peer-to-peer
– Cooperative group work
– Promotion of active participation of all students
Previous knowledge:
– Universe and planet Earth.
– Materials, colours, geometry and volumes.
– Geography: relief, rivers, oceans.
– History: The first great civilizations, Mesopotamia, and Egypt.
Materials:
Computer and projector.
Various materials for the construction of the model such as: cardboard, black cardboard, acrylic paints, white glue,…
Phase 1 Duration: 20 minutes

Several circles by Wassily Kandinsky,1926
Development:
The project will start with the visualisation of Several Circles by W. Kandinsky. Some scaffolding questions regarding what they observe are suggested. The idea is that the initial visualisation leads towards a specific question:
“Have you ever thought if humans are alone in the universe?”
Then they will be invited to become astronomers for the Spatial European Agency and do spatial observations.
Phase 2 Artistic action & experimentation Duration: 9 hours

Development:
1. In groups of 3 or 4 students reflect about the following topics to define:
a) The imagined planetary system.
Inspired by the milky way system they have to develop their own system. Is important that the teacher provides feedback to their students, suggestion questions and/or consequences in their planetary system. E.g., What implications have the fact that the system has two suns? Is there two mons, how will they rotate. Will they eventually collide?
b) The characteristics of the habitable planet of this imagined system
What makes a planet feasible to live in?
Distance of the sun, the presence of water, oxygen, gravity? Students with the help of the professor and their previous knowledge have to reflect on the question.
c) The characteristics of the first historical civilization of this of this imagined planet: habitats, palaces, temples, means of transport, religious beliefs.
Based on ancient civilization they have already studied, students imagine a civilization
2. Elaboration of the digital book based on what they have decided previously.
During the whole process, a digital book remains as a tool to collect and share the discovering done of the planetary system. Is preferred to work with online collaborative tools in order for them to share easily the work between them, but also grating access to internet to get inspiration and/or ideas.
3. Elaboration of the model with its solar system and a fragment of the imagined planet.
Linked with the art, students have to represent a visualization. A suggestion on the materials is offered, but also the option for the students to bring the material they feel necessary to bring.
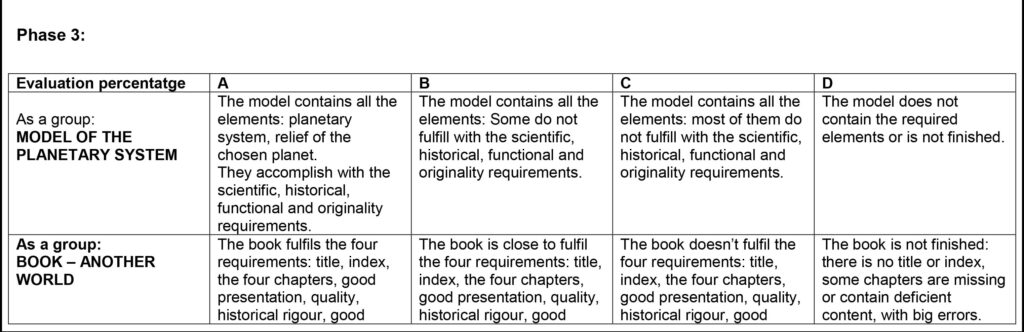
Phase 3: Reflexion and debate Duration: 2 hours and 40 min.
Development:
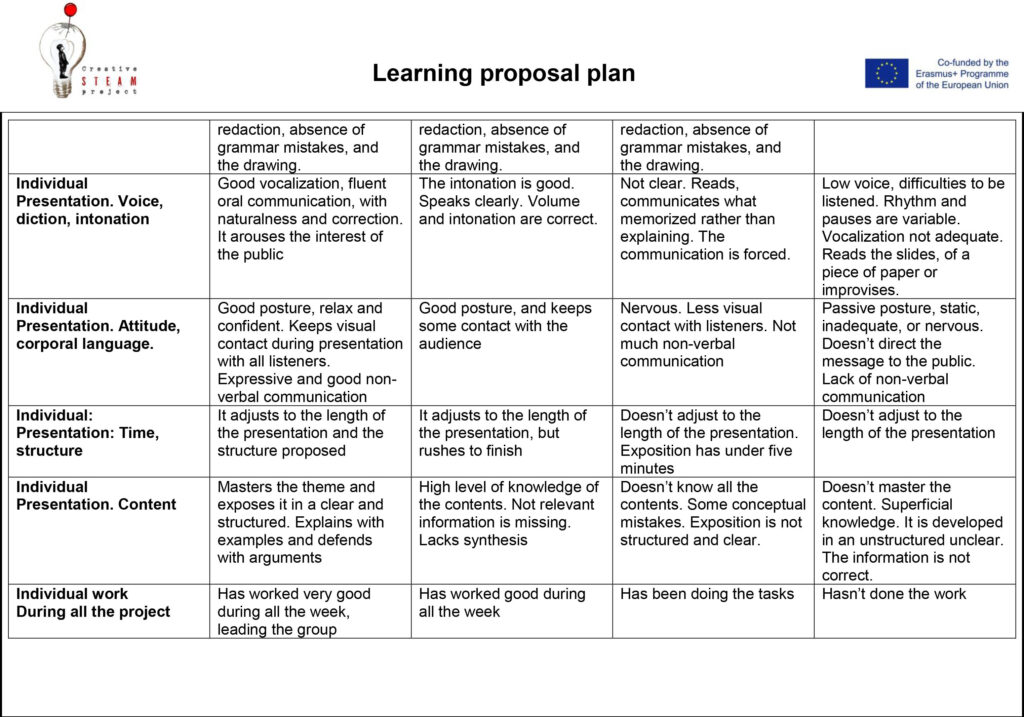
4. Oral presentation of their discovery (5 ‘)
Is part of the evaluation process of their learnings. An exhaustive proposal is offered in the Reference and Links subsection
5. Delivery of the book and the model
The book, the compilation where they collected the information for Spatial European Agency, is delivered. It contains an exhaustive information Οf the planetary system. The oral presentation should be a summarize of the information contained in this book.
The model, a representation of they have observed, is shared with their peers.
Both Book and Model are subject of evaluation, and a proposal of its evaluation can be observed in the references and links subsection.
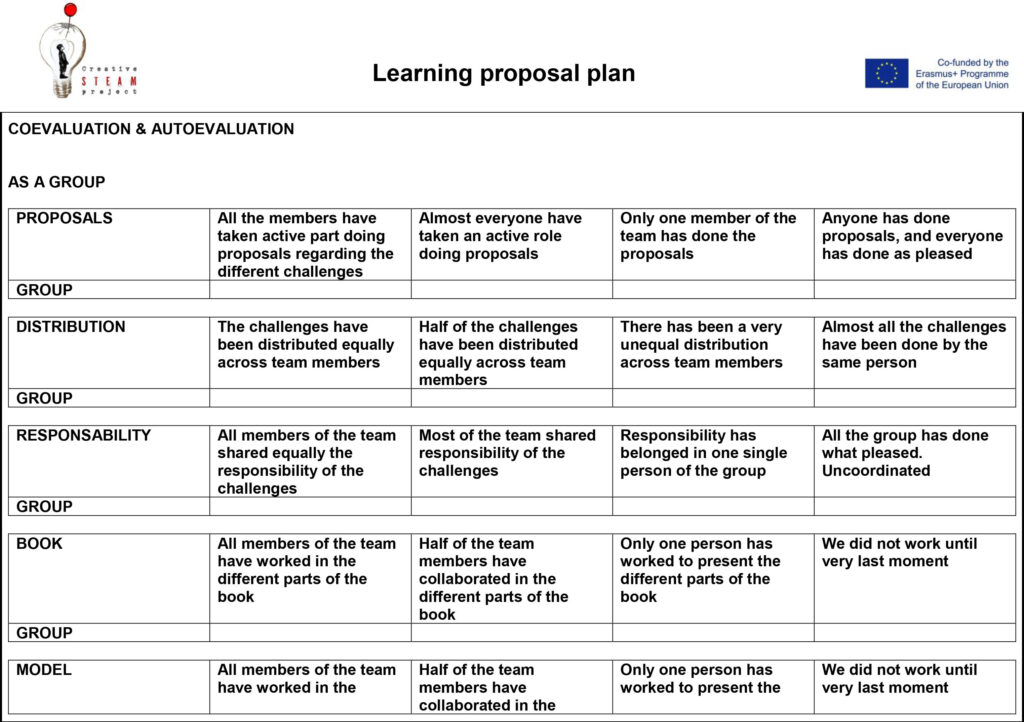
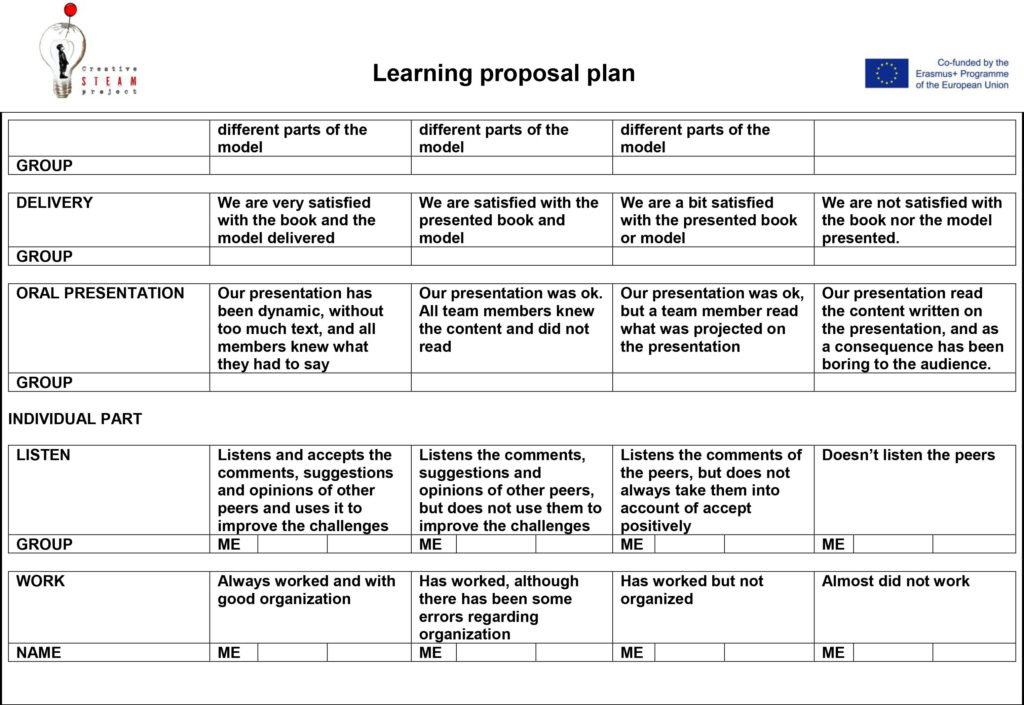
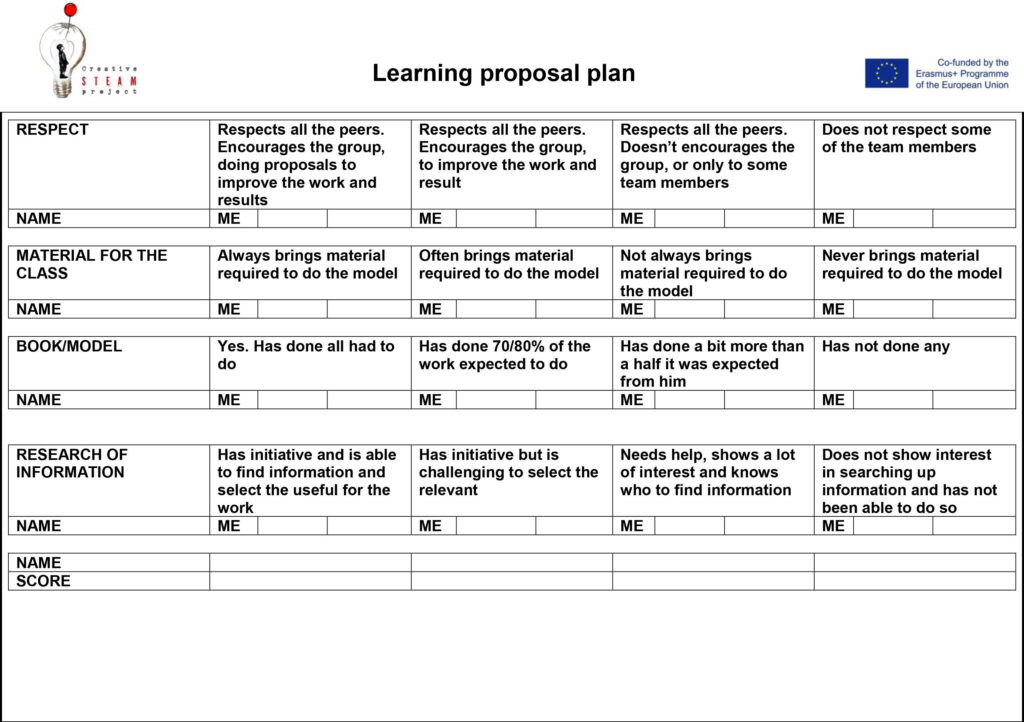
6. Autoevaluation and coevaluation
A grid of the autoevaluation and coevaluation is provided to orient them. If can be find in the reference and links subsection. Furthermore, a constructive co evaluation is highly advised. A Simple form to execute it is with tops & tips. A good way to remark the strong points of the planetary system they provided, but also the points that could have been improved.
Comments, possible derivations, and prolongations of the proposal:
If an example of an alternative civilization is required, some pieces of universal literature can be briefly exposed. An easy example is Utopia by Thomas More (1516). The information regarding the civilization is easily found and can be helpful for them to imagine the first point in the development phase.
Tools to provide an easier co evaluation and auto evaluation (for students and teachers), is highly advised. The suggestion is using Corubrics (https://www.corubrics.org/) The tool is available in different languages, including English.